Introduction to Functional Safety Management & Safety Instrumented Systems
introduction
Functional safety management and safety instrumented systems are crucial in various industries, ensuring the safety of employees, the public, and the environment. These areas provide a framework for analyzing and evaluating risks and taking necessary precautions to prevent accidents and harm.
Functional safety management involves applying principles and practices for designing and operating industrial systems to handle various hazardous scenarios and ensure safe operation. Safety instrumented systems are a part of this work, providing an additional layer of protection by using specialized equipment and technology for control, alarms, and intervention in processes when incidents occur.
These fields are essential for industries dealing with hazardous processes and systems, such as the petrochemical, oil and gas, automotive, and other chemical industries. They aim to achieve the highest levels of safety and reliability in industrial operations, often adhering to international standards and regulations, such as the IEC 61508 standard, to ensure the implementation of best practices in this domain.
Agenda:
- Safety, Risk, and ALARP
- Functional Safety Scope
- Functional Safety Standards
- Introduction to Safety Life Cycle; and
- Quick intro to SIL Assignment and Verification
What is safety?
The condition of being safe mast be Freedom from danger, risk, or injury Safety is the state of being “safe” The condition of being protected from harm or any other event which could be considered non-desirable.Freedom from Unacceptable Risk
What is your unacceptable risk?
In safety and risk management, unacceptable risk usually refers to a level of risk that is deemed too high or dangerous to be acceptable by certain standards, and actions should be taken to reduce or mitigate that risk. The criteria for what constitutes unacceptable risk can vary widely depending on the context, industry, and specific circumstances. It’s a subjective judgment made based on factors like the potential consequences, the likelihood of occurrence, and the societal or organizational norms
Achieving Safety:
In most situations, safety is best achieved by an inherently safe process design If necessary, this may be combined with protective systems to address any residual identified risk.
When protective measures are combined with inherent safety consideration should first be given to passive then active protection systems.
Protective systems can rely on different technologies – Chemical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic, thermodynamic and programmable electronic.
Protection Layers (Onion Rings):
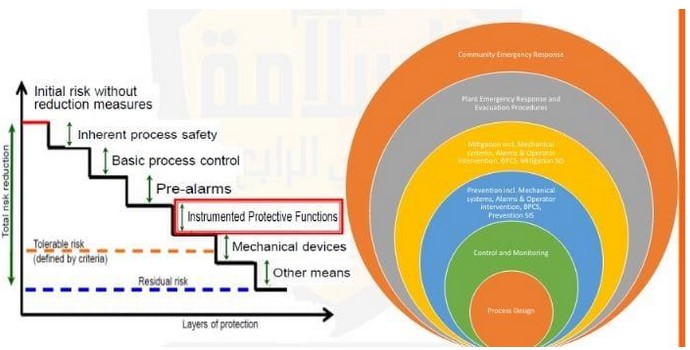
Scope of a Safety Instrumented Function:
An SIF is a critical component designed to reduce the risk of a hazardous event to an acceptable level by taking appropriate actions in response to process deviations or failures.
The scope of a Safety Instrumented Function is a critical element in the overall safety management of an industrial process. It ensures that the SIF is designed and implemented to effectively mitigate specific hazards and contribute to a safer working environment.
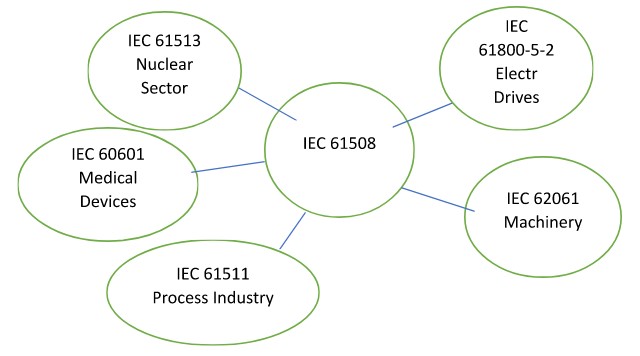
Functional Safety Standards:
Any safety related device/system-based E/E/PE Technology
Any Safety related systems in any industry sector including Process, Nuclear, Oil & Gas, Exploration, Sub Sea, Aerospace, Military , Railway
- IEC 61508
- IEC 61513 Nuclear Sector
- IEC 61800-5-2 Electr Drives
- IEC 62061 Machinery
- IEC 61511 Process Industry
- IEC 60601 Medical Devices
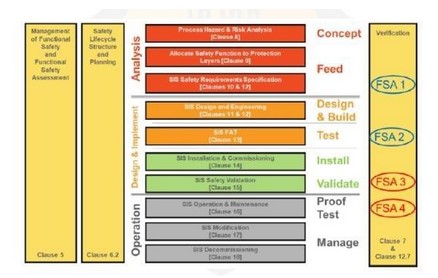
What is Safety Integrity?
Safety Integrity is the Ability of the SIS to perform the required SIF as and when required.
The Ability includes both the functional response and the likelihood that the SIS will act as required.
Safety Integrity requirements are the set of the IEC 61511 requirements which shall be satisfied by a SIF to claim a given Safety Integrity Level (SIL) for a SIF.
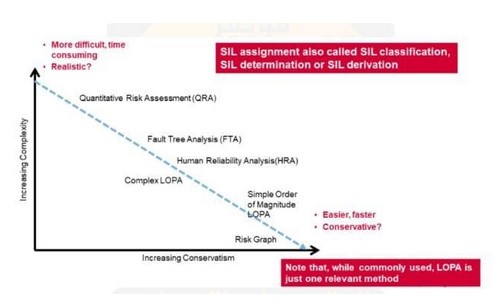
SIL Assignment:
SIL Verification:
- SIL Verification involves verifying that SIS design meets all requirements and achieves SIL target during SIL assignment.
- SIL level based on Systematic Capability (SC) of each device used in a SIF.
- SIL level based on minimum architecture constraints (SILac) for each element (subsystem) in a SIF.
- SIL level based on a PFH (high demand), or a PFDavg (low demand) for the entire SIF
The End !
In summary, functional safety management and safety instrumented systems are vital in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of industrial processes. They help identify and mitigate risks, protect personnel and the environment, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, ultimately contributing to a safer working environment.
















